1.Appointment-based consultations, reduced waiting time
- Non-public hospitals generally adopt appointment systems and streamlined consultation processes, allowing patients to schedule specialist visits in advance and avoid long queues.
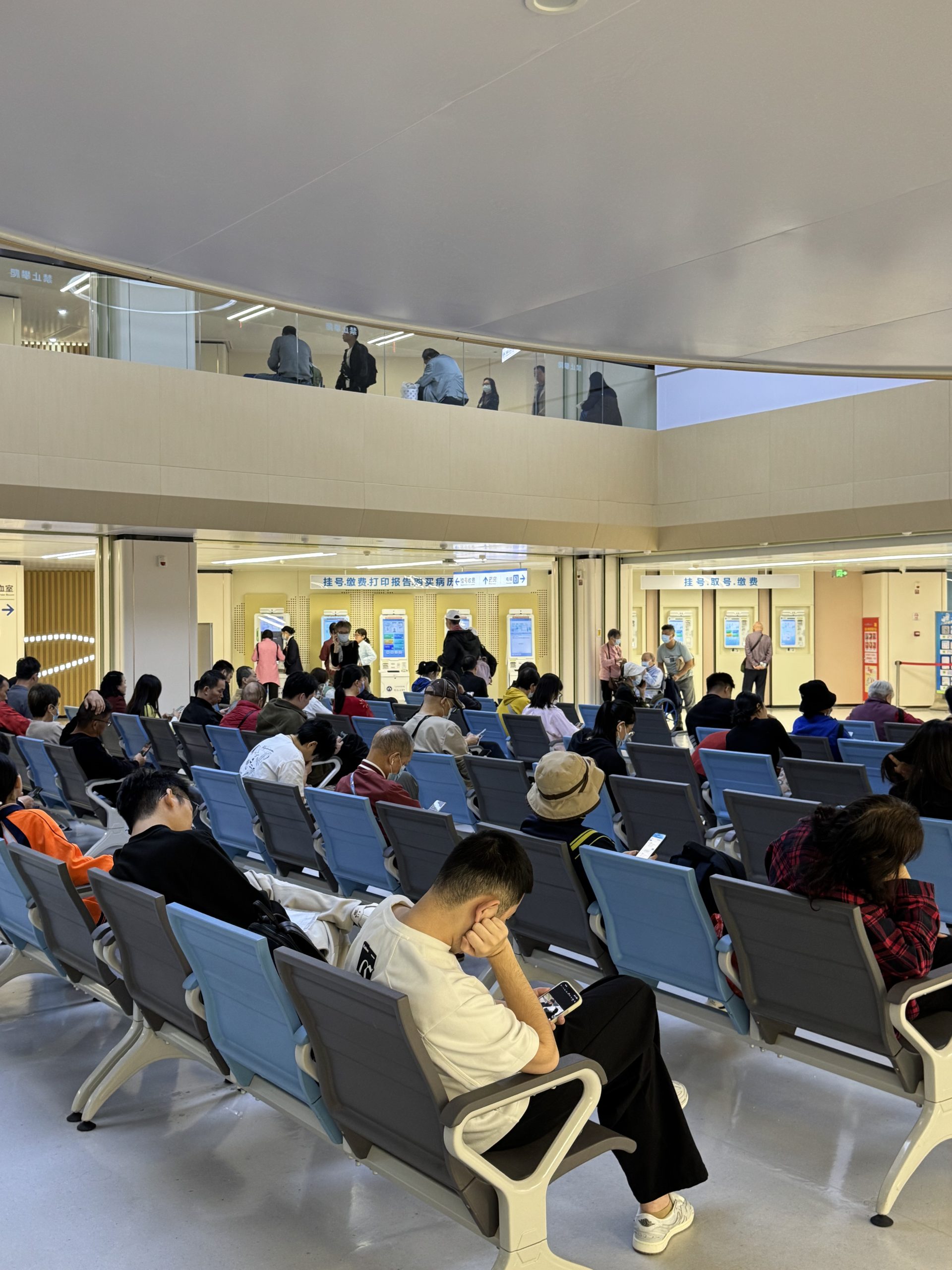
- In contrast, public Tier-3 hospitals often face high patient volumes, long queues, and extended waiting times.
2.Ample inpatient beds, no hospitalization pressure
- Non-public hospitals have sufficient bed availability, so patients can be admitted without long waits.
- Public Tier-3 hospitals often experience bed shortages, especially in popular departments or for critically ill patients, sometimes requiring inter-hospital transfers.
3.High-end and comfortable patient rooms
- Non-public hospitals provide VIP or five-star standard rooms, featuring private bathrooms, TV, Wi-Fi, and catering services.
- Public hospitals focus on functionality, with less comfort and privacy in their wards.
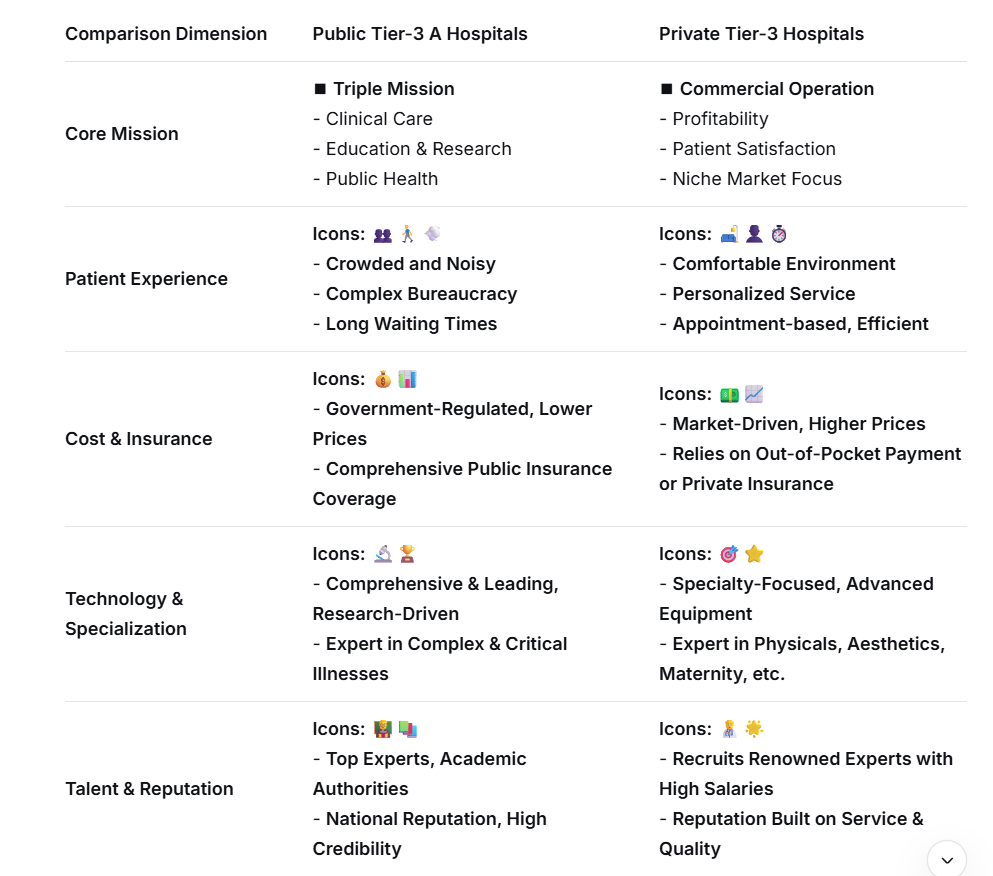
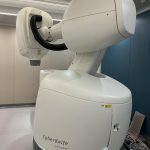
4.Advanced medical equipment and technology
- With flexible investment, non-public hospitals can quickly introduce state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment equipment (e.g., MRI, CT, PET-CT, Da Vinci surgical robots).
- Public hospitals’ equipment upgrades depend on government budgets, and some high-end instruments may lag behind.
5.Personalized service and patient care
- Healthcare teams emphasize one-on-one care, health management, and rehabilitation guidance, offering private doctors or full-service patient management.
- In public hospitals, staff resources are tight, and services are often standardized.
6.Fast examination and treatment process
- Non-public hospitals offer integrated examination, reporting, and diagnosis, enabling patients to complete tests and consultations within a day or short period.
- In public hospitals, testing and reporting often require separate appointments and longer waiting times.



发表回复